Yes, you heard it right.
A new version of COMpfun remote access trojan (RAT) has been discovered in the wild that uses HTTP status codes to control compromised systems targeted in a recent campaign against diplomatic entities in Europe.
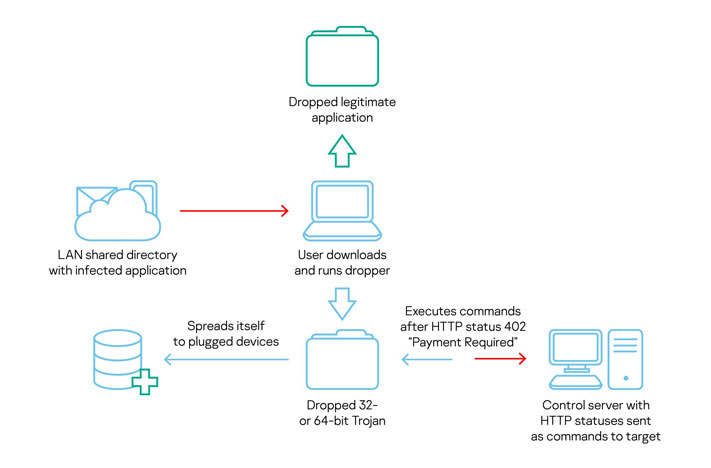
The cyberespionage malware—traced to Turla APT with "medium-to-low level of confidence" based on the history of compromised victims—spread via an initial dropper that masks itself as a visa application, the Global Research and Analysis Team at Kaspersky discovered.
The Turla APT, a Russian-based threat group, has a long history of carrying out espionage and watering hole attacks spanning various sectors, including governments, embassies, military, education, research, and pharmaceutical companies.
First documented by G-Data in 2014, COMpfun received a significant upgrade last year (called "Reductor") after Kaspersky found that the malware was used to spy on a victim's browser activity by staging man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks on encrypted web traffic via a tweak in the browser's random numbers generator (PRNG).
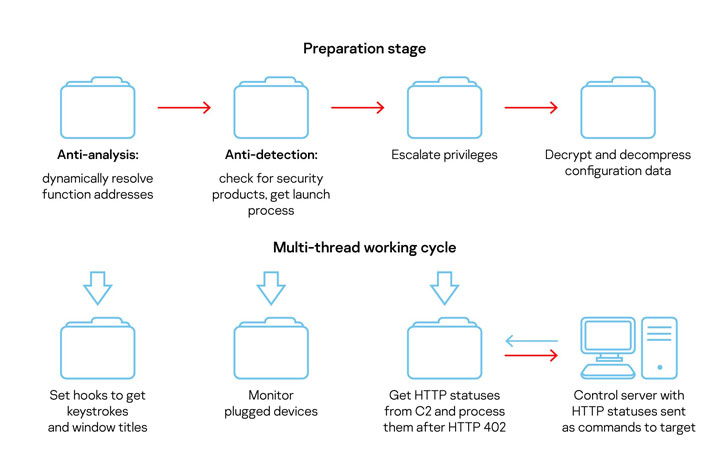
In addition to functioning as a fully-featured RAT capable of capturing keystrokes, screenshots, and exfiltrating sensitive data, this new variant of COMpfun monitors for any removable USB devices plugged to the infected systems to spread further and receives commands from an attacker-controlled server in the form of HTTP status codes.
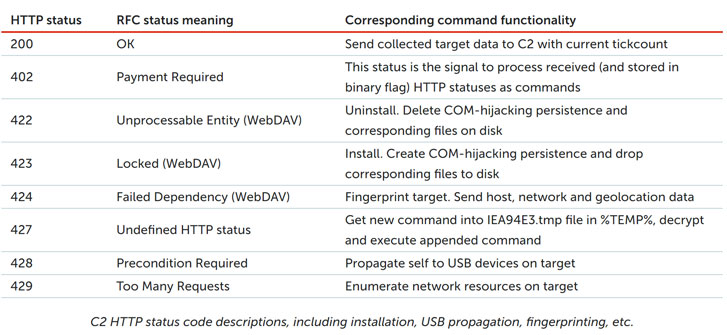
"We observed an interesting C2 communication protocol utilizing rare HTTP/HTTPS status codes (check IETF RFC 7231, 6585, 4918)," the researchers said. "Several HTTP status codes (422-429) from the Client Error class let the Trojan know what the operators want to do. After the control server sends the status 'Payment Required' (402), all these previously received commands are executed."
HTTP status codes are standardized responses issued by a server in response to a client's request made to the server. By issuing remote commands in the form of status codes, the idea is to obfuscate any detection of malicious activity while scanning internet traffic.
"The authors keep the RSA public key and unique HTTP ETag in encrypted configuration data. Created for web content caching reasons, this marker could also be used to filter unwanted requests to the C2, e.g., those that are from network scanners rather than targets."
"To exfiltrate the target's data to the C2 over HTTP/HTTPS, the malware uses RSA encryption. To hide data locally, the Trojan implements LZNT1 compression and one-byte XOR encryption."
While the exact modus operandi behind how the malicious visa application is delivered to a target remains unclear, the initial dropper, upon download, runs the next stage of malware, which communicates with the command-and-control (C2) server using an HTTP status-based module.
"The malware operators retained their focus on diplomatic entities, and the choice of a visa-related application — stored on a directory shared within the local network — as the initial infection vector worked in their favor," Kaspersky researchers concluded.
"The combination of a tailored approach to their targets and the ability to generate and execute their ideas certainly makes the developers behind COMpfun a strong offensive team.
"The authors keep the RSA public key and unique HTTP ETag in encrypted configuration data. Created for web content caching reasons, this marker could also be used to filter unwanted requests to the C2, e.g., those that are from network scanners rather than targets."
"To exfiltrate the target's data to the C2 over HTTP/HTTPS, the malware uses RSA encryption. To hide data locally, the Trojan implements LZNT1 compression and one-byte XOR encryption."
While the exact modus operandi behind how the malicious visa application is delivered to a target remains unclear, the initial dropper, upon download, runs the next stage of malware, which communicates with the command-and-control (C2) server using an HTTP status-based module.
"The malware operators retained their focus on diplomatic entities, and the choice of a visa-related application — stored on a directory shared within the local network — as the initial infection vector worked in their favor," Kaspersky researchers concluded.
"The combination of a tailored approach to their targets and the ability to generate and execute their ideas certainly makes the developers behind COMpfun a strong offensive team.
Source: The Hacker News
Comments
Post a Comment